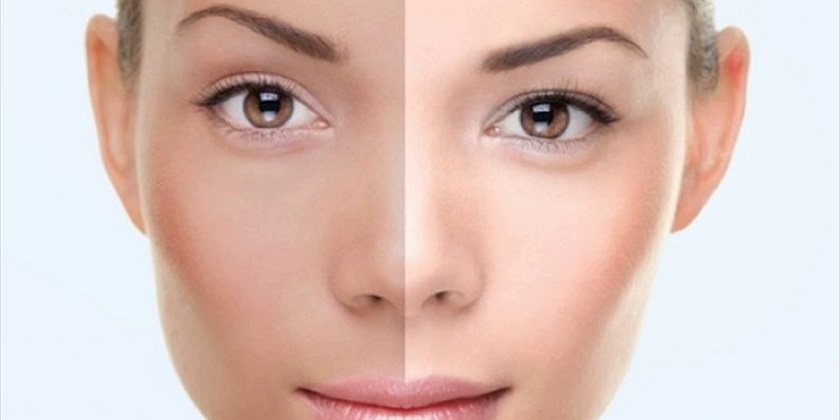


Hyperpigmentation is the name that healthcare professionals give to patches of skin that become darker than surrounding areas of skin.
Types of hyperpigmentation include age spots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Each of these has a different cause and a range of treatments and products, including creams and cosmetic procedures. We discuss these below.
Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces more melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. This can make spots or patches of skin appear darker than surrounding areas.
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition. It affects people of all skin types.
Some forms of hyperpigmentation, including melasma and sun spots, are more likely to affect areas of skin that face sun exposure, including the face, arms, and legs.
Other types of hyperpigmentation form after an injury or skin inflammation, such as cuts, burns, acne, or lupus. These can occur anywhere on the body.
Having extra pigment in some areas of skin is usually harmless but can sometimes indicate another medical condition.
Although hyperpigmentation is harmless, some people wish to get rid of it. There is a range of possible treatment methods and home remedies that people can try.
To prevent hyperpigmentation, or to stop it from becoming more prominent:
People can try the following treatments to lighten dark patches of skin and remove hyperpigmentation:
Many people use topical treatments to treat hyperpigmentation. Topical treatments will include ingredients that lighten the skin, such as:
Some cosmetic procedures can also lighten areas of skin to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
Cosmetic procedures for hyperpigmentation include:
People who are considering undergoing one of these procedures should discuss the process and possible side effects with a skin care specialist or dermatologist.
The cause of hyperpigmentation depends on the type. The most common causes of hyperpigmentation are:
The body produces more melanin to protect the skin from prolonged exposure to the sun. This can cause dark spots or patches on the skin called age spots or sun spots.
Areas of skin can darken after people have had inflammation of the skin. This can include acne, eczema, lupus, or an injury to the skin. People with darker skin are more likely to develop post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Darker patches of skin can form when people experience hormonal changes. This type of hyperpigmentation is common during pregnancy.
Certain medications, such as antimalarial drugs and tricyclic antidepressants, can cause hyperpigmentation. In these cases, patches of skin may turn gray.
Chemicals in topical treatments can also sometimes cause hyperpigmentation.
More serious causes of hyperpigmentation include Addison's disease and hemochromatosis.
Addison's disease affects the adrenal glands. It can cause hyperpigmentation in certain areas of the body, including:
Other symptoms of Addison's disease include:
A person should see their doctor if they notice any of these symptoms.
Hemochromatosis is an inherited condition that causes the body to contain too much iron. It can cause hyperpigmentation, making the skin appear darker or tanned.
A person should see their doctor if they notice the following symptoms of hemochromatosis: