
Fungal infections are common throughout much of the natural world. In humans, fungal infections occur when an invading fungus takes over an area of the body and is too much for the immune system to handle.
Fungi can live in the air, soil, water, and plants. There are also some fungi that live naturally in the human body.
Like many microbes, there are helpful fungi and harmful fungi. When harmful fungi invade the body, they can be difficult to kill, as they can survive in the environment and re-infect the person trying to get better.
In this article, we take a look at who is most at risk of getting a fungal infection and what the symptoms and treatment options are for some common types.
The symptoms of a fungal infection will depend on the type, but common symptoms include the following:
Read on to find out more about some common types of fungal infection, their symptoms, and the treatment options.
The following conditions are all common types of fungal infections.
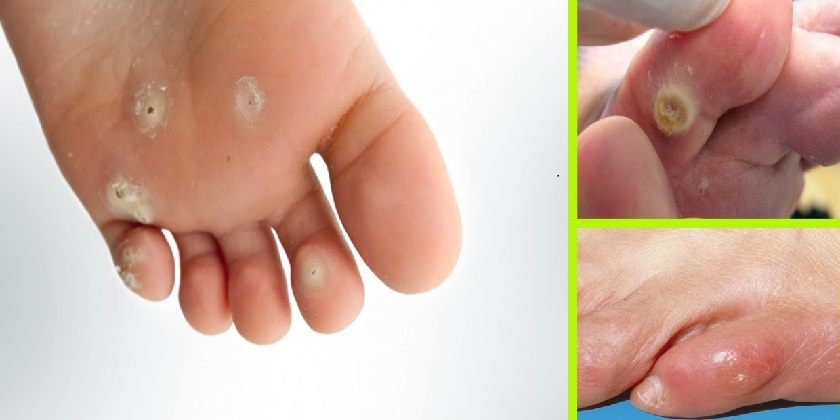
Tinea pedis or athlete's foot is a common fungal infection that affects the foot.
Athlete's foot is commonly associated with sports and athletes because the fungus grows perfectly in warm, moist environments, such as socks and shoes, sports equipment, and locker rooms.
In reality, anyone may be affected by athlete's foot. It is most common in warmer climates and summer months, where it can quickly multiply.
Vaginal yeast infections are a common form of Candida overgrowth in women, usually caused by Candida albicans.
An overgrowth of Candida disrupts the normal balance of the bacteria and yeast in the vagina. This imbalance of bacteria may be due to antibiotics, stress, and hormone imbalances, or poor eating habits, among other things.
Candida infections can also commonly cause fungal toenail infections and diaper rash.
A rash may develop over time in some cases. Yeast infections should be treated quickly, as the symptoms may become severe if left untreated.
Tinea cruris, commonly known as jock itch, is another common fungal skin infection.
These fungi love warm and damp environments and thrive in moist areas of the body, such as the groin, buttocks, and inner thighs. Jock itch may be more common in summer or in warm, humid areas of the world.
Jock itch is mildly contagious and is often spread through direct contact with an infected person or an object that is carrying the fungus.
Tinea corporis or ringworm is a skin infection caused by a fungus that lives on dead tissues, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Ringworm is the fungus that causes both jock itch and athlete's foot. When it appears anywhere else on the body, the infection is just called ringworm.
Ringworm is highly contagious, and it can be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact, or from contact with pets, such as dogs. The fungus may also survive on objects, such as towels, clothes, and brushes.
The ringworm fungus also infects soil and mud, so people who play or work in infected dirt may catch ringworm as well.
Fungal infections are common in humans and are usually not very serious if they are treated quickly and correctly.
Anyone with a weakened immune system may be more likely to contract a fungal infection, as well as anyone who is taking antibiotics.
Cancer treatment and diabetes may also make a person more prone to fungal infections.